April 17th, 1853 marks the day that President Domingo Faustino Sarmiento of Argentina officially made it his mission to transform Argentina’s wine industry. Malbec has gone from the replacement for Merlot (early to pronounce, attractively fruit-forward, including a good shellac of vanilla-scented oak, produced on a massive scale and value-priced) to examples that are more focused, more site-specific, and well-crafted to show their terroir.
April 17th, 1853 marks the day that President Domingo Faustino Sarmiento of Argentina officially made it his mission to transform Argentina’s wine industry. Malbec has gone from the replacement for Merlot (early to pronounce, attractively fruit-forward, including a good shellac of vanilla-scented oak, produced on a massive scale and value-priced) to examples that are more focused, more site-specific, and well-crafted to show their terroir.
In honor of this holiday, I pulled a few bottles to refresh my markers. The two Malbecs I tasted were from the homeland of Malbec (Cahors, France) and the homeland in the New World (Mendoza, Argentina).
Malbec markers:
Overall, the wines are deep garnet with a distinctly pink (sometimes neon) rim and staining tears. In both examples, dark fruits lead the way with medium+ body and balanced alcohol (13.0-13.5%), and what stood out to me was the elevated levels of bright acidity that lifted the mid-palate.
Cahors markers: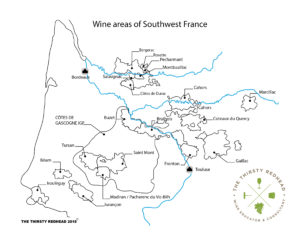
Cahors is upriver from Bordeaux on the River Lot, and Malbec is a minor blending partner in Bordeaux, but otherwise, this region has nothing to do with them. Cahors has to be a minimum of 70% Malbec (called Cot here), and the rest can be Merlot and/or Tannat. I love that they “soften” Malbec here with Tannat. My example here was 80% Malbec and 20% Merlot.
Compared to the Mendoza example, the character of the dark fruits was pure, and the aromas were all about savory things: leather, bloody, bitter chocolate, and organic earth. It had bright acidity , but the tannins were more dried herbal/edgy/savory. It is definitely a wine for lovers of old world styles and would show best with food (especially something gamey).
Mendoza markers: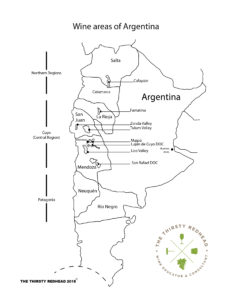
This region is too large to make sweeping generalizations about the climate or soils, and this is might be one of the reasons why Malbec has become a consistently successful brand it is today. With so many micro-terroirs to blend from, you can be assured that you will have a clean, varietally correct glass of wine. I have seen more of a focus on these micro-terroirs lately.
Very fruit forward (to let you know that this is from the New World), the dark fruits of plums and blueberries were cooked (almost candied) and framed by chocolate notes, violet florals, and a hint of mint (or alcohol? The label said 13.0%). But compared to Cahors, this was all about generous and attractive fruits. Again, bright acidity lifted the soft dark fruits, and tannins were more ripe/resolved tannins. Very easy to drink.
Laterals: Syrah, Merlot, and Dão
When I miss Malbec, I usually have Syrah or Merlot. I can also throw a red from the Dão in there. My tasting partner threw in Greanche, but the color and the acidity was off.
 Malbec Versus Syrah: Similar color, including pink (though more purple on the Syrah) rim and staining tears. Dark fruits on the nose were also similar, but there were a lot of savory elements in the Syrah that I think are unique to it. For instance, the Cahors shows a lot of savory notes (leather/meaty), and Syrah typically shows meaty/smoky notes. But there’s an olive and mint/eucalyptus that I associate strongly with Syrah. Also, while the Syrah was leading with dark plums, there were also red fruits here.
Malbec Versus Syrah: Similar color, including pink (though more purple on the Syrah) rim and staining tears. Dark fruits on the nose were also similar, but there were a lot of savory elements in the Syrah that I think are unique to it. For instance, the Cahors shows a lot of savory notes (leather/meaty), and Syrah typically shows meaty/smoky notes. But there’s an olive and mint/eucalyptus that I associate strongly with Syrah. Also, while the Syrah was leading with dark plums, there were also red fruits here.
Malbec has some tannins, but Syrah has massive tannins. The chunky tannins on the Syrah carried the fruit through to the finish while the Malbecs were more balanced between the fruits and the texture of the tannins.
In a blind situation, I would consider Syrah for the color, cooked dark fruits, savory elements, and medium+ acidity. But the tannins here are massive, and the aromas include very distinctive Syrah markers like the olive, smoke, and mint. By comparison, the Mendoza Malbec was all about fruits and spice, and the Cahors was all about savory notes and savory tannins.
Malbec Versus Merlot: The color on the Merlot, while deep, was not as inky as the Malbecs and did not have any pink or staining tears. I always get in trouble using color as an absolute funnel though. Merlot has intense dark fruits but a lot of red fruits as well. Like I said above, I don’t typically get a lot of red fruits out of Malbec but more dark plum and blueberry. That said, there was a sweetness to the Merlot fruit that harkens to Malbec, but it was not candied as in the Mendoza example. The elevated amount of tannins was similar to Malbec but had only moderate acidity in this example of Merlot.
I have often mistaken Merlot for Malbec, and I’m updating my funnel to point out that Merlot has dark and red fruits. Really pay attention to the mid-palate. Malbec has a bright acid lift across your tongue while Merlot has a plump coating of fruit across the tongue (with acidity framing that fruit on the sides). Tell me if you agree.
 Malbec Versus Dão: This wine shares the deep ruby color of the Malbec, but the rim is also ruby (nothing pink about it). Like the Cahors, there is a strong savory and meaty note dominating the nose of the Dão, but instead of that organic earth, it was more of a stony minerality. (I typically find a lot of granite notes in all wines from Portugal.)
Malbec Versus Dão: This wine shares the deep ruby color of the Malbec, but the rim is also ruby (nothing pink about it). Like the Cahors, there is a strong savory and meaty note dominating the nose of the Dão, but instead of that organic earth, it was more of a stony minerality. (I typically find a lot of granite notes in all wines from Portugal.)
The Dão had the dark fruits that both Malbecs show but none of the chocolate, and I did find red fruits as well for the Dão (more dried strawberries and cherries) where there were not a lot of red fruits in any of the Malbecs. The palate on the Dão was distinctive with pronounced acidity (even higher than the Malbecs) with massive, coarse tannins. Even the Cahors with its more rustic/savory tannins were finer in texture by comparison.
My funnel will now say that there are more red fruits, pronounced acidity, and massive tannins of native Portuguese grapes in the Dão that make it different from the Malbec.
Other laterals I have written down over the years include Tannat and Petit Verdot for the inky color and massive tannins, but I am finding that Malbecs today show more resolved tannins than I had originally thought. I also have Bonarda as a possible lateral for the acidity, but Bonarda doesn’t show the purple tints of Malbec nor the candied fruit (actually, my Bonarda note reads more like Barbera!). These kinds of laterals are going down the rabbit hole… Go for the obvious.
 Malbec Rosé:
Malbec Rosé:
No need to adjust your screen. That is the correct color. Bright pink, almost cotton candy in color (White Zinfandel is a lateral on color alone). This makes sense when you remember that the two Malbecs above both had a neon pink meniscus. The rosé here had generous dark fruits, especially blueberry, and a touch of earth (though not mineral). Tried as I did, I did not get any red fruits at all. That’s a marker. Similar medium+ amount of juicy acidity found in the still red versions with a bit of dissolved CO2 to help lift the fruits. It was full-bodied for a rose and not quite bone dry. The tech sheet said 13% abv, and the bottle was printed at 14.5% (I thought it was something in between).
So, those are my markers and laterals. I hope you found it useful. Crack a bottle (or several) of Malbec tonight, and tell me what your markers and laterals are.